Glycine is denoted as Gly or G, which is one of the proteinogenogen amino acids used to make protein in the body, especially the collagen found in skin, ligaments, muscles, bones, and cartilage. Glycine accounts for about 35% of the collagen in the human body. Glycine also helps regulate nerve impulses in the central nervous system and digestive system. Glycine helps with the breakdown of fats by adjusting the concentration of bile acids. Glycine is also needed for heme biosynthesis. Heme is an important component of hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is essential in maintaining red blood cell integrity and optimal oxygen transport capacity. Unlike other amino acids derived primarily from the foods we eat, glycine can be synthesized in the body, and therefore it is not considered an essential amino acid. With many health benefits, We need to get glycine supplements from protein-rich foods like meat, poultry, fish, eggs, milk, beans, and cereals.


1. Top 5 Glycine health benefits
1.1 Glycine health benefits: Helps produce antioxidants


✅ Glycine is one of the 3 amino acids your body uses to make glutathione, a powerful antioxidant that helps protect your cells against oxidative damage caused by free radicals. The condition of not having enough glycine will lead to less glutathione production, which can negatively affect the body, causing the body to resist oxidation that damages cells over time.
✅ A 2011 study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that glutathione deficiency in the elderly improved with the addition of the precursor glutathione cysteine and glycine. This helps increase concentration and reduce oxidative stress, reducing oxidative damage that leads to aging. In some studies, glycine has even been found to help prevent cell mutations that lead to cancer.
1.2 Glycine health benefits: Promotes muscle growth


✅ Glycine is one of the amino acids necessary for creatine biosynthesis. Creatine provides muscles with a direct source of energy and helps build muscle tissue and strength. It also helps to fuel cells thanks to its role in converting nutrients from your diet, helping to grow muscle tissue, enhancing endurance, strength, and performance.
✅ It is also helpful for patients recovering from surgery or other causes of motor difficulties because it can help prevent muscle degeneration. Glycine has been shown to help inhibit the decline of valuable muscle tissue formation and enhance muscle recovery. In fact, it’s called an “anti-aging amino acid” because it helps maintain muscle mass as age increases, stimulates growth hormone secretion, prevents fatigue, and even improves daytime energy, workout performance, and uplifting.
1.3 Glycine health benefits: Glycine is the main amino acid in collagen


✅ Along with other amino acids in bone broth (especially proline), glycine plays an important role in collagen formation, promoting the growth and function of the skin, blood vessels, joints, tendons, and ligaments. About 1/3 of collagen is made up of glycine.
✅ Glycine (through the consumption of collagen) significantly improves skin elasticity in older women, improving skin moisture and dehydration. Hydrolyzed collagen is beneficial in preventing UV-B from damaging skin and aging skin. Women taking 2.5g of collagen for 4 weeks reduced 20% of eye wrinkles and had a lasting effect after the study ended. By week 8, collagen has significantly improved skin elasticity by up to 65%. Glycine slows down the effects of aging by improving the body’s use of antioxidants, while also building muscle, which helps firm, healthy skin.
1.4 Glycine health benefits: Glycine helps protect the liver

✅ Excessive consumption of alcohol can have detrimental effects on the body, especially your liver. There are three types of alcohol-induced liver damage:
- Fatty liver: An accumulation of fat inside the liver, which increases the size of the liver.
- Alcoholic hepatitis: The cause of long-term, excessive drinking.
- Alcoholic cirrhosis: The final stage of alcoholic liver disease, which occurs when liver cells are damaged and scar tissue form.
✅ Research shows that glycine may reduce the harmful effects of alcohol on the liver by preventing inflammation. This has been shown to reduce blood alcohol levels in alcohol-consuming mice by stimulating the metabolism of alcohol in the stomach rather than the liver, thereby preventing the development of fatty liver and alcoholic cirrhosis. Studies on the effects of glycine on alcohol-induced liver damage are currently limited to animals, and glycine needs to be studied more than human effects.
1.5 Glycine health benefits: Nervous system support


✅ Glycine helps regulate the metabolism of several nutrients that the brain and nerves use. It helps regulate nerve impulses throughout the body by balancing electrolyte levels, such as calcium, chloride, and potassium. Because of its role in nerve function and neurotransmission, glycine also helps improve sleep, uplifting, improving mood, memory, and behavior.
✅ Because of its role in the central nervous system and digestive system, glycine can be used to ease anxiety or stress that keeps you awake at night and help you sleep better. According to research by the Japanese Sleep Research Association, glycine supplements help improve sleep quality, reduce daytime sleepiness, and improve the performance of memory tasks.
✅ In addition, it also supports the treatment of mental illness. Glycine supplementation for 5 years can significantly reduce the symptoms of OCD (obsessive-compulsive disorder) in adults. Glycine supplementation significantly reduces symptoms of schizophrenia. In patients with schizophrenia, it helps to improve cognitive symptoms. Glycine helps treat schizophrenia by increasing the intermediate neurotransmission through the NMDA receptor and it is used along with psychiatric medications.
2. Foods that contain Glycine
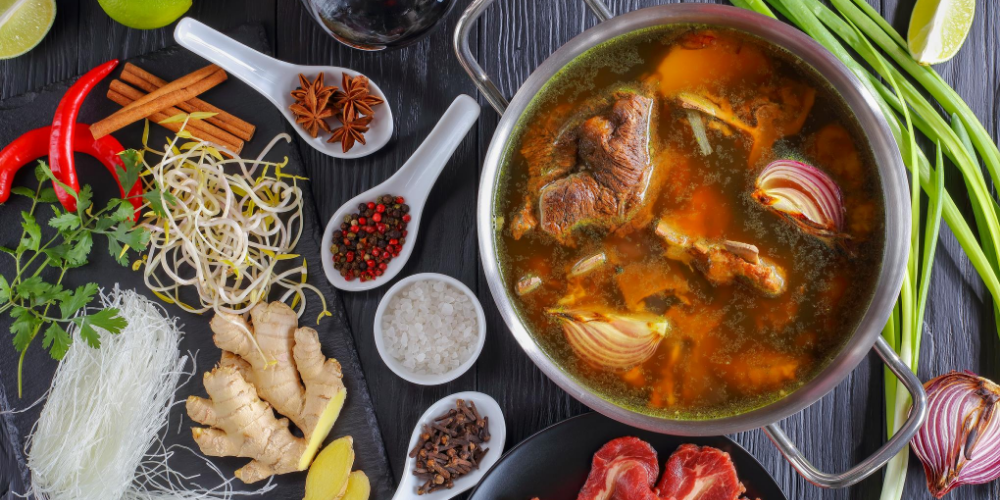


- Getting glycine from your diet is easier than you think. Bone broth is a great source of natural glycine and other amino acids, inexpensive, simple to make, and has many health benefits. Bone broth is made from animal parts including bones, skin, and tendons that contain natural collagen, releasing important amino acids and other substances that are often lacking in the diet.
- However, if you do not like using bone broth, you are vegetarian or vegan, you can get glycine from plant foods. Glycine-rich plant sources include beans, vegetables like spinach, kale, cauliflower, cabbage, and pumpkin; fruits like bananas and kiwi. Unlike bone broth, glycine can also be found in “complete protein sources” (animal proteins), including meat, dairy products (yogurt, fresh cheese, ice cream), poultry, eggs, and fish.
3. Notes when using Glycine
If you can’t get glycine from food, you can use supplements. When using this format, you should note the following:
- When taking glycin, you may experience some of the following side effects: nausea, vomiting, stomach discomfort, drowsiness.
- There are no daily recommendations of glycine. It is believed that most people get about 2 grams of glycine daily from the diet. Depending on the symptoms you are seeking to resolve, you may use it as directed by your doctor.
Recommended for you
🎁 NOW Supplements, Glycine 1,000 mg Free-Form, Neurotransmitter Support


✅ 1968 Since 1968 NOW has been a leader in the natural products industry. Even when healthy foods and natural supplements weren’t mainstream, we’ve never wavered from our mission – to provide value in products and services that Empower people to lead healthier lives.
✅ Glycine is the smallest and simplest amino acid, making it versatile for use in a wide range of functions. Glycine is necessary for the production of glutathione, DNA, creatine, bile, hemoglobin, and most proteins. It also helps to promote glycogen storage, thereby making glucose readily available for energy production. Glycine also functions as a calming neurotransmitter in the brain, where it facilitates nerve impulses and is important for the maintenance of healthy sleep patterns. Directions: Take 1-3 capsules daily, preferably on an empty stomach. Store in a cool, dry place after opening.






Leave a Reply