
What is Inflammation?
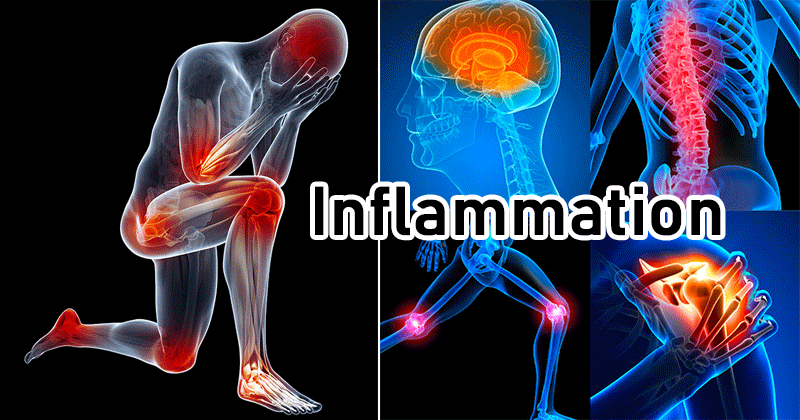
Before we can look closely at foods that fight inflammation, let us first understand what inflammation is. The inflammation process is one of the ways in which the immune system and the white blood cells react to pathogens such as viruses, bacteria, and fungi. During a major injury to your body, your body triggers scarring, which helps in healing. However, in case you have arthritis, your body may trigger an inflammatory response even when pathogens are absent. Such ‘autoimmune’ diseases like arthritis cause your immune system to attack your own body cells, which then wreaks havoc in your body. While some physical symptoms of inflammation may include your body becoming red, being swollen, hot, having chills, fatigue, loss of appetite, headaches, and muscle stiffness, in some cases, these symptoms may not manifest themselves, which makes it very hard for you to even know if you are suffering from inflammation.
Inflammation is believed to play a role in heart disease, obesity, and cancer, and is mostly triggered by foods rich in sugar and saturated fats. These food substances make the immune system overactive, contributing to fatigue, joint pain, and damage to blood vessels. By adopting a diet rich in foods that fight inflammation, you can counter toxins and free radicals.
Top foods avoid inflammation
1. Vegetables
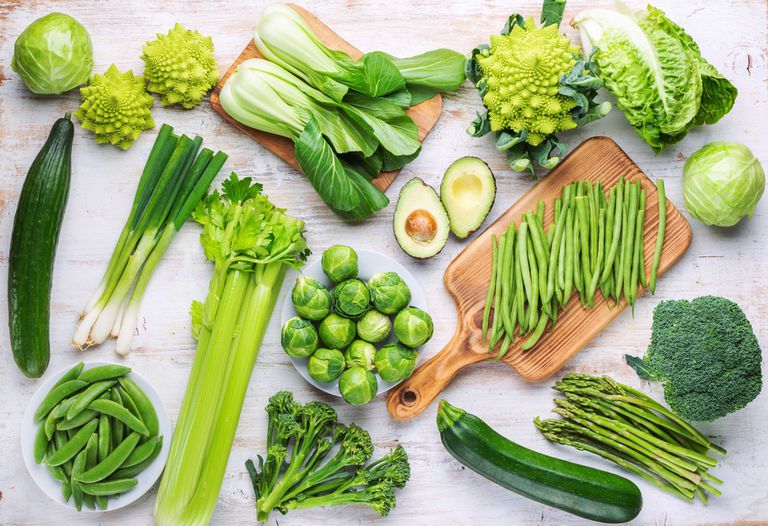

Collard greens. These dark leafy vegetables are rich in vitamin E, which protects the body against cytokines, pro-inflammatory molecules. Collard greens are rich in minerals such as iron and calcium, and phytochemicals that fight diseases.
Celery is rich in vitamin C, an antioxidant, and other phenolic antioxidants that act as anti-inflammatory agents. Antioxidants help in reducing the oxidative damage to the body fat and minimize the risk associated with oxidative damage to the blood vessel walls. Your cells are shielded away from the free radicals (free radicals are dangerous products that are produced from various metabolic activities). Celery also contains manganese and beta-carotene.
Kale is rich in sulfur, a mineral that allows your liver to carry out the two-detox cycles required in the body. The second cycle allows the body to produce more phase II enzymes to breakdown toxins in a similar manner to how digestive enzymes work. The second phase is important in detoxifying the body by lowering the accumulation of toxins.
Red cabbage has an anti-inflammatory phytonutrient known as anthocyanin, and a good quantity of polyphenols that combat oxidative stress and inflammation.
Broccoli. This nutritious vegetable contains kaempferol and sulforaphane, phytonutrients that fight cancer and inflammation. The substances reduce oxidative stress and inflammation, fight allergy and eliminate cancerous toxins from the body. Broccoli is also rich in vitamin C, an antioxidant. Add steamed or raw broccoli florets to salads, soups or use as garnish. Do not overcook broccoli to avoid killing the active ingredients.
Beans. As opposed to meat that may contain antibiotics, steroids, or hormones, beans are a healthy source of protein that is rich in antioxidants. Try to reduce intake of animal proteins by replacing with beans, and as a form of anti-inflammatory diet.
Beets. This red-colored veggie contains antioxidant properties both in the beet and beetroot juice, and is a good remedy for heart disease and cancer. Beets are rich in vitamin C, hearty helping fiber and betalains, a plant pigment.
Tomatoes. This is considered a nightshade vegetable, as may help some people fight inflammation though might not work for others. The red and juicy tomatoes are rich in lycopene, an active ingredient against inflammation in the lungs and other body parts. Research found out that cooked tomatoes had more lycopene than raw ones, meaning that tomato sauce is more recommendable. Drinking tomato juice is also effective.
Spinach is rich in carotenoids, an antioxidant that fights inflammation.Spinach also contains vitamin E. If you want to serve spinach, first steam for a few minutes to facilitate digestion.
2. Fruits
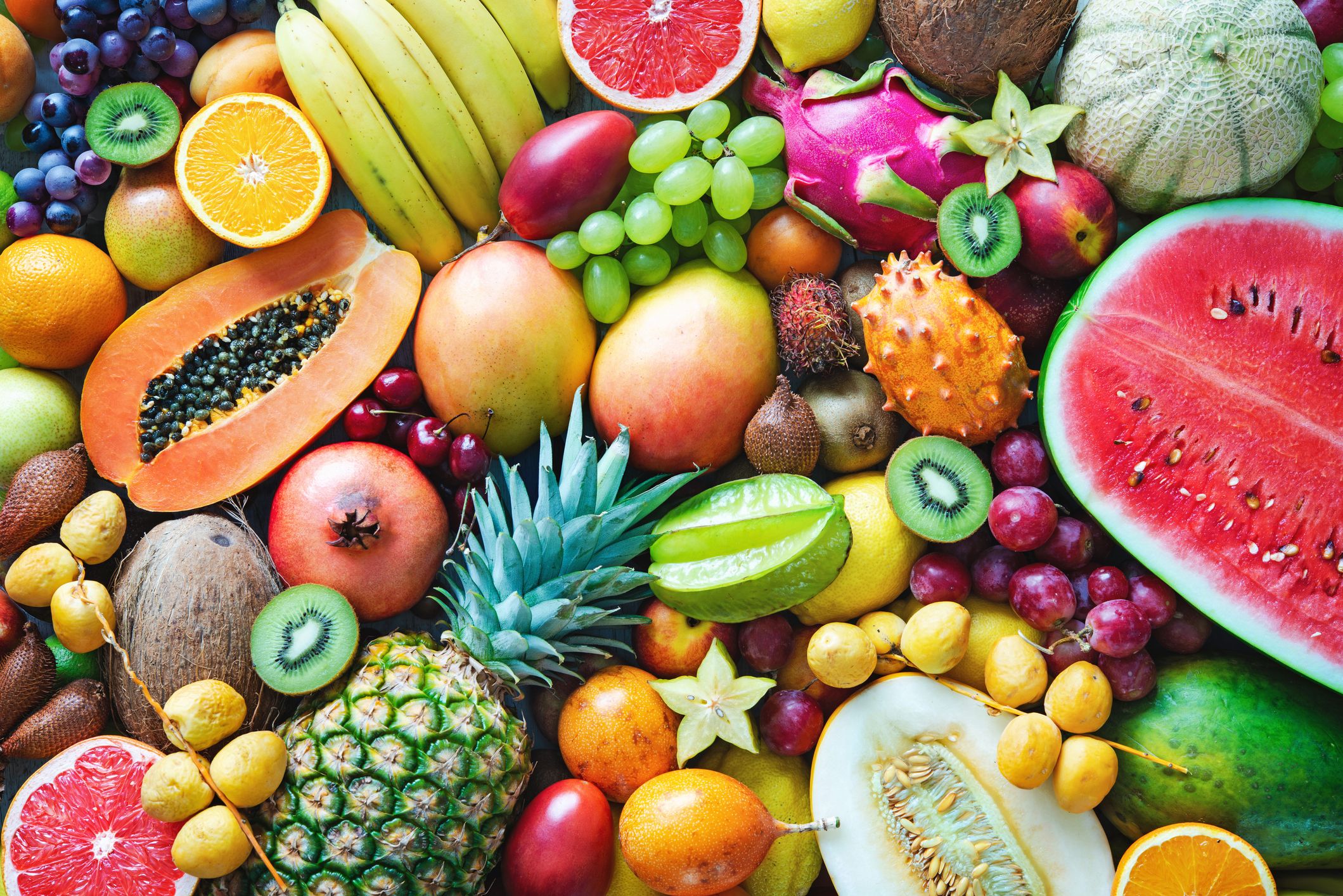

Avocados contain a number of anti-inflammatory substances, among them vitamin C and E, omega 3 fatty acids and minerals such as zinc, selenium and manganese. They also contain phytosterols and carotenoid antioxidants among them alpha-carotene, beta-carotene and lutein. To eat more avocados, include them in desserts, dressings, raw soups and salads.
Cranberries contain phytonutrients that heal your cardiovascular system and other parts of the digestive system such as colon, stomach, gums and mouth. Add cranberries to desserts, salad dressings, and smoothies, either when fresh or frozen.
Blueberries are rich in phytonutrients among them hydroxycinnamic acids, anthocyanins and flavanols. These substances work as anti inflammatory and antioxidants compounds in your body. Add blueberries to salads, cakes, pies and smoothies, or eat the wild and organic berries.
Papaya contains vitamins C, E and beta-carotene, which has the antioxidant properties of papaya. It also contains protein-digesting enzymes such as chymopapain and papain, which also fight inflammation.
Tart Cherries contain anthocyanins, antioxidants that fight inflammation. They work up to 10 times better than aspirin, and are effective in reducing risk of heart disease. Tart cherries are reported to help athletes reduce intake of inflammatory pain meds and thus improve their performance. They can minimize pain from post exercise soreness and arthritis, and has shown to possess the highest antiinflammatory properties compared to other food. The recommendable daily intake of tart cherries is a cup of tart cherry juice or 1-½ cups of tart cherries.
Pineapples possesses an anti-inflammatory substance known as bromelain, which is effective in reducing pain, bruising, and swelling. You can incorporate pineapple into your workout smoothie, or add to a savory stir-fry.
Red/Purple/Green Grapes. Different varieties of grapes have antioxidants among them resveratrol and flavonoids, which possess the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. For instance, resveratrol has shown power to fight ailments ranging from Parkinson and Alzheimer’s diseases to cancer and aging.
3. Herbs, Seeds and Spices
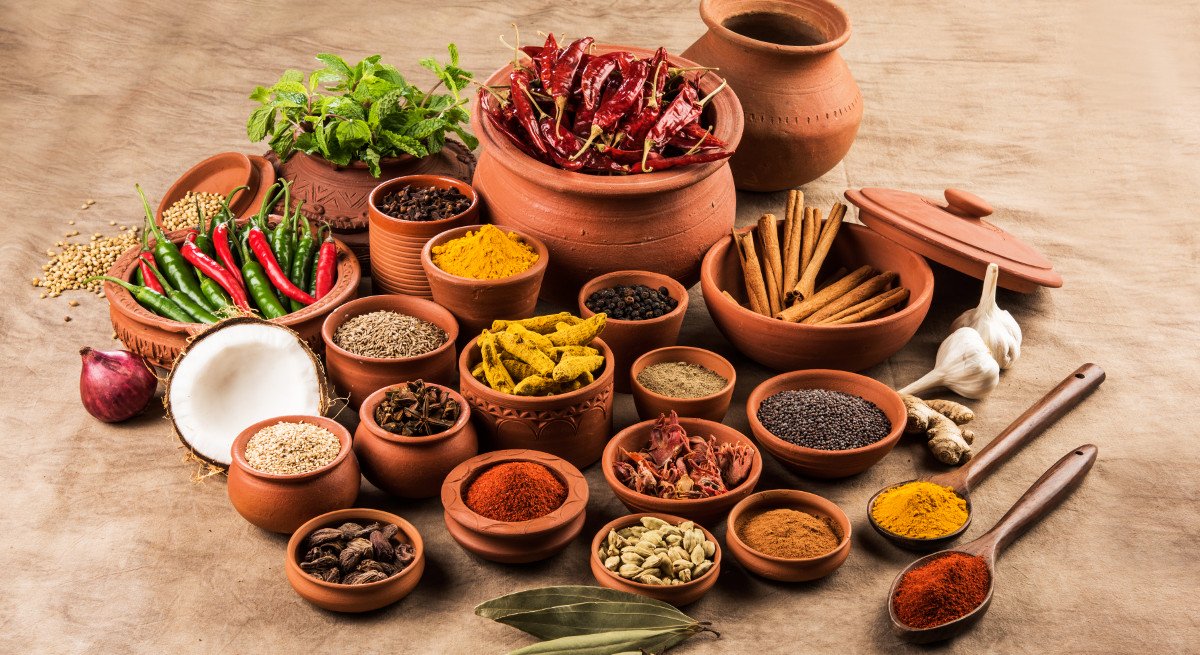

Basil. This herb has a good amount of antioxidant phytonutrients, where you just need a sprinkle of basil to get the benefits.
Hemp seeds are rich in omega 3 fatty acids, and unsaturated fats that fight inflammation. Hemp seeds also contain gamma-linolenic acid, a form of omega-6 fatty acid, and functions as an inflammatory messenger. You can add hemp seeds to desserts, cereals, smoothies, or sprinkle in soups and salads.
Chia seeds. The black seed contain more omega-3 fatty acids compared to salmon, and does not pose health risks associated with hormones found in fish or heavy metals from seawater. Omega 3 fatty acids are very effective in inflammation. You can add chia seeds to your pudding, cereals and to smoothies.
Turmeric contains curcumin, an active ingredient that offers the anti-inflammatory properties. Curcumin has shown potential to relieve arthritis pain, stomach ulcers, Irritable Bowel Syndrome, and the Crohn’s disease. Turmeric also contains magnesium, vitamin B6, and iron, which contribute to healthy immune system and functioning red blood cells. The spice can be added to rice, smoothies, soups and curries.
Flaxseed contains alpha-Linolenic acid and lignans, making it a great remedy against inflammation. Flaxseed also contains a good amount of omega 3 fattyacids, which you can obtain by a small dash added to various meals.
Peppers. Chili and Cayenne Hot Peppers are rich in capsaicin, an active ingredient that fights pain and inflammation. However, peppers may worsen rheumatoid arthritis in some patients, thus should be taken with caution.
Ginger. Various scientific researches found ginger to contain gingerols, an antiinflammatory substance that fights swelling, and muscular pain. Ginger also contains antioxidant properties, which work hand in hand with gingerols. You can use ginger in teas, smoothies, salad dressings, soups and juices.
Olive Oil contains polyphenols, which reduce the level of C-reactive protein in the body. Extra virgin olive oil possesses antioxidants together with oleic acid, a fatty acid that fights inflammation. You can use olive oil on salads, grain dishes, and hot pasta or on pizza.
Garlic and Onions. Onion has a compound known as allicin that releases sulfenic acid, a free radical fighting agent. It also has a phytonutrient quercetin, an antioxidant that helps the body combat inflammation. Onion is best used in greens, eggs, and grain dishes. Garlic also possesses anti-inflammatory properties from the sulfur compounds that facilitate the immune system fight inflammation.
4. Nuts
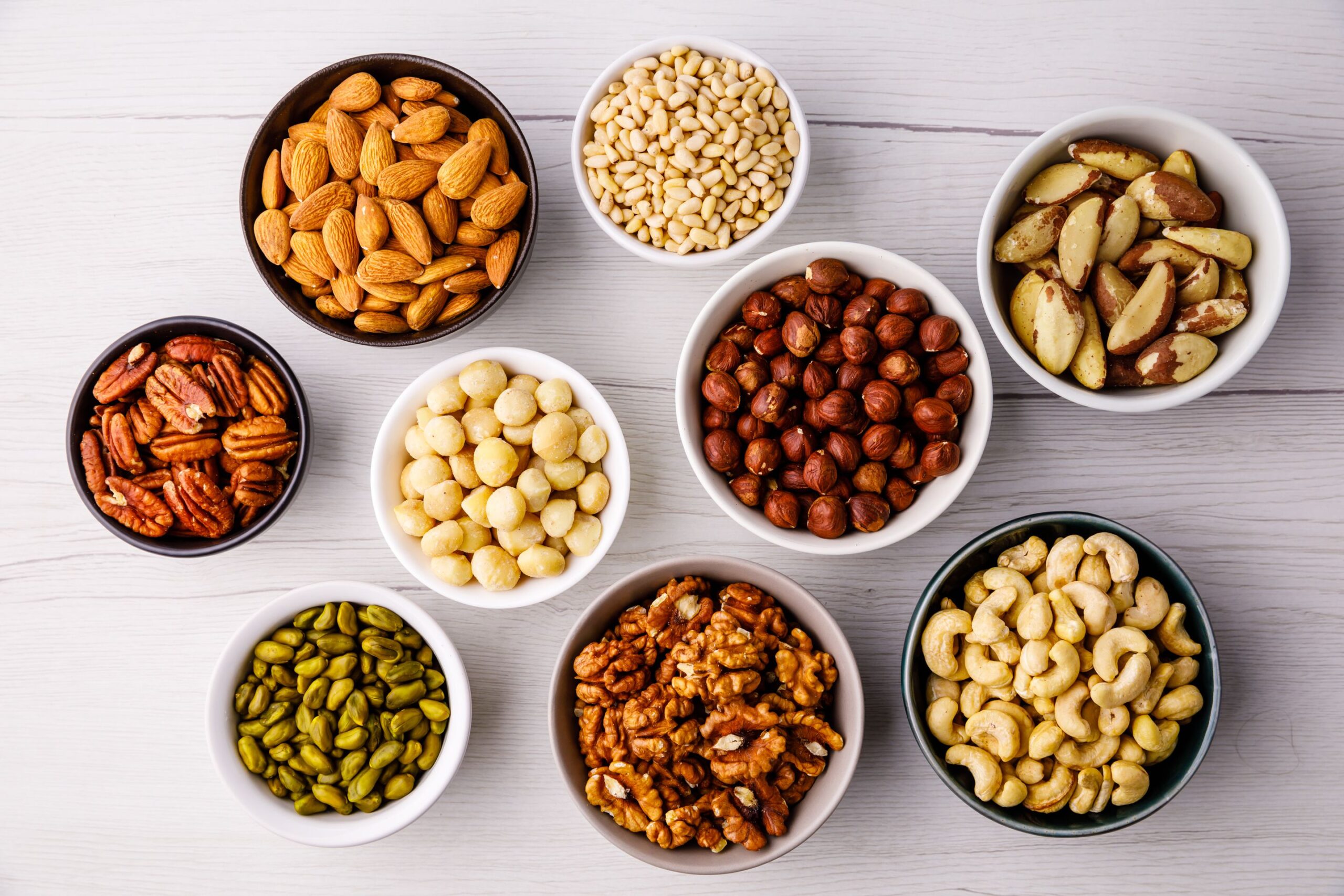

Walnuts are high in alpha-linolenic acid, which is a precursor to omega-3 fatty acids such as EPA and DHA in your body. Intake of the acid has indicated the ability to sooth inflammation and thus reduces cell damage. However, nuts are high in fat content and thus should be eaten in moderation.
Almonds is full of vitamin E, calcium, and fiber; nutrients that are needed to keep inflammation at bay. To get more benefits, you can incorporate almonds with fish, whole grains, and leafy greens, which form the Mediterranean diet. The diet is effective in fighting inflammation within 6 weeks.
Raisins. Though appearing wrinkly, a raisin has been found to lower the marker of inflammation that is known as TNF-alpha.
5. Other Important Foods

Whole Grains contain fiber, which is needed to counteract the effect of Creactive protein, a marker of inflammation in the blood. Look for natural grains that do not contain added sugars, such as oats, brown rice and brown bread. Also, minimize intake of refined grains such as pasta, white bread, rice and cereals.
Shiitake Mushrooms. As opposed to other mushrooms, this variety has polysaccharides that offer relief and protection from inflammation. Replace your ordinary mushrooms with these to obtain the benefits.
Shellfish such as scallops, oysters, and shrimp are good for inflammation. Shrimp is rich in astaxanthin, an active ingredient that makes it a more effective shellfish. However, moderate their intake as shellfish contain cholesterol.
Soy Products contain isoflavones, an estrogen-like compound that helps to lower inflammation level in women. Soy is also reported to reduce the inflammation levels in heart and bones. To enjoy benefits of soy, avoid heavily processed variety as it has additives that aren’t healthy for the body. Go for tofu, soymilk, and boiled soybeans.
Low-Fat Dairy. Various milk products trigger autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, especially if you suffer allergies or intolerances to casein, a protein is found in milk. In case you can tolerate casein, go for low fat or non-fat dairy to get the required nutrients. Some yoghurt products contain probiotics, bacteria fighting compounds meant to fight gut inflammation. Low-fat milk should also supply vitamin D and calcium, for healthy heart, reduction of cancer risks and bone strength.
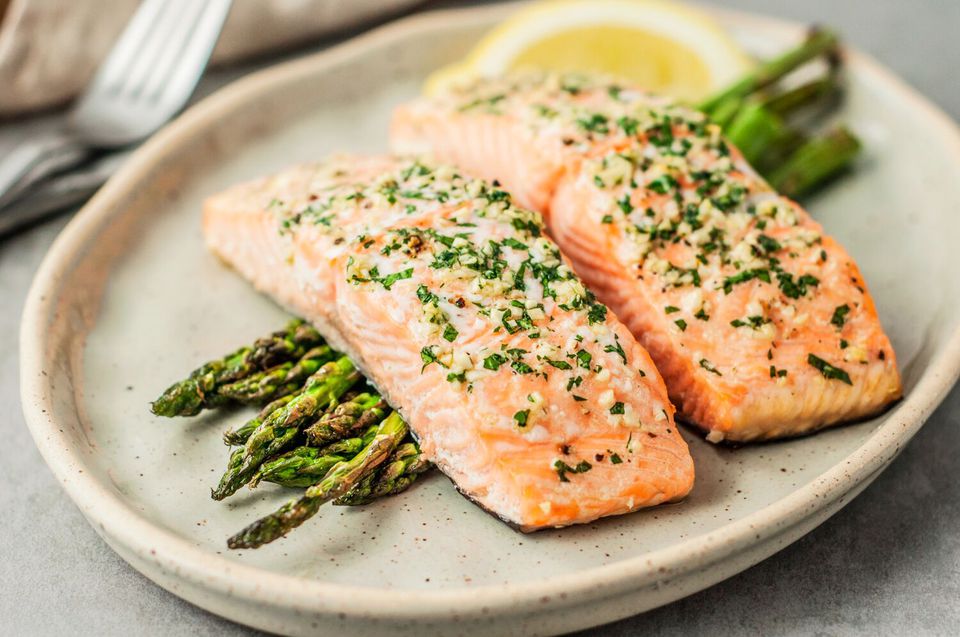
Fatty fish. The fish with the highest amount of Omega-3 fatty acids are sardines, tuna, mackerel and salmon, which are effective in fighting inflammation. To fight inflammation successfully, you need fish a number of times a week, being cooked in healthy ways. According to a research, eating boiled or baked fish was found to be more effective in healing the heart disease as opposed to eating salted, dried, or fried fish. In case you don’t like fish, try out fish oil supplements. To balance the amount of omega 6 to omega 3 fatty acids, just take a fifth teaspoon fish oil to a teaspoon of omega-3 fatty acids.
Sweet Potatoes. These are nutrient packed, being very healthy for your immunity, skin and heart health. Sweet potatoes are also great at fighting inflammation, as they are rich in vitamins C and E, beta carotene, alpha-carotene and carotenoids. Other related foods to look for are carrots, apricots, cantaloupe, and pumpkins, which are good sources of vitamins and carotenoids.







Leave a Reply